Application Security
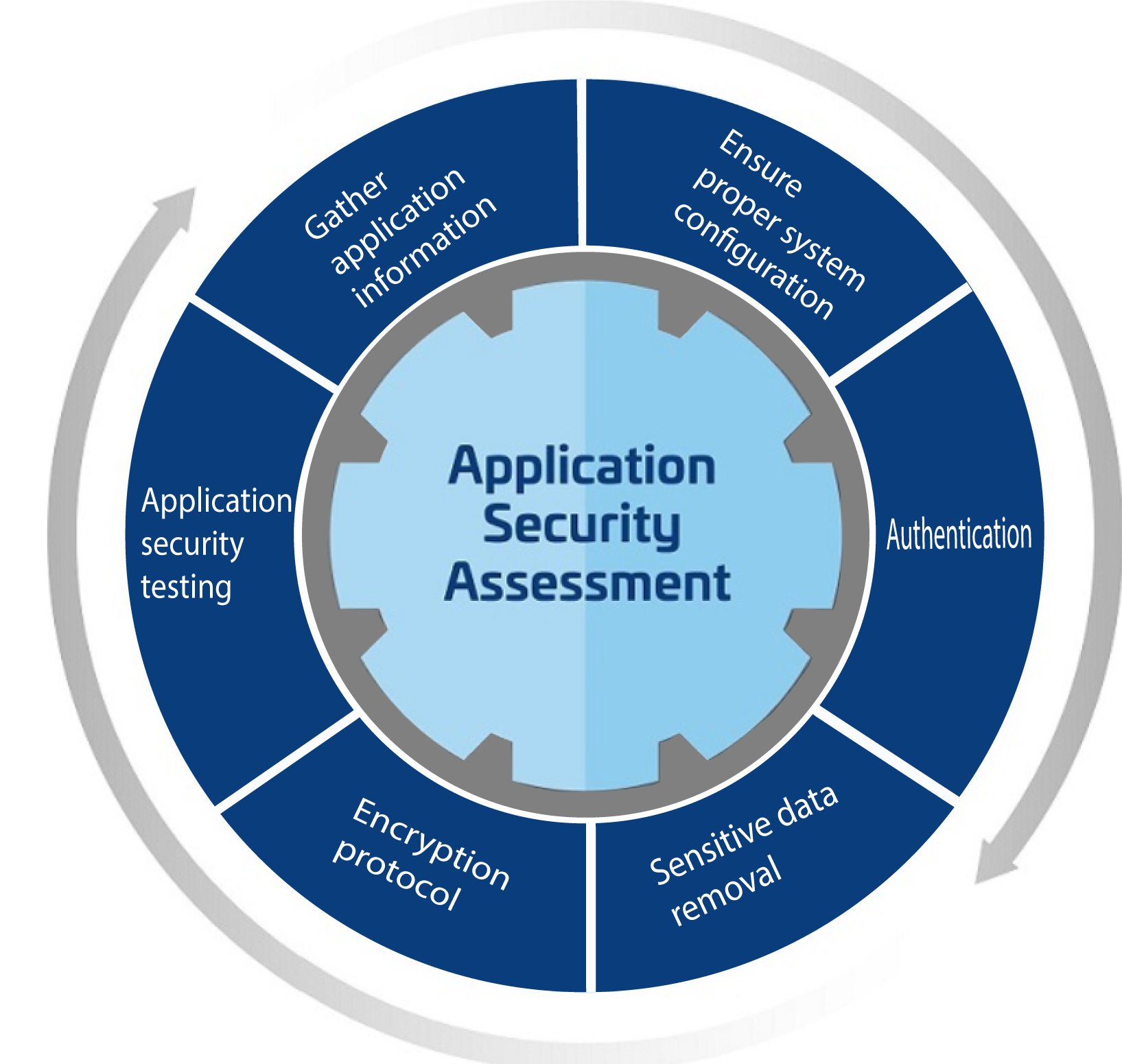
Preventing Application vulnerabilities.
SQL Injection
Type of phishing scam in which fraudsters impersonate company executives.
Cross Site Scripting
Account takeover fraud refers to a form of identity theft, where attackers steal users’ credentials.
Cross-site request forgery (CSRF)
A fraudster telling you that supplier payment details have changed with alternative details.
Broken Authentication
Insider fraud is fraud committed by someone who is on the “inside. Its one of the most devastating.
Cyber Risk Quantification
Why Application Security
Share the Financial Impact of Cyber Risk with the Business and Prioritize What Matters the Most. Better business decision-making and collaboration happens when you can translate cyber risk into financial terms that every business stakeholder can understand. RQ is an automated cyber risk product that computes cyber risk in monetary terms. RQ’s automation of complex cyber risk calculations enables conversations with the business around the value of security in terms they can understand.
Design and Develop your application securely
We protect your applications with Test Scanning all your end points.
Application security helps to reduce the risk of data breaches, financial losses, and damage to a business's reputation. Additionally, having secure applications can help to meet compliance requirements, such as those set by government regulations, industry standards, and customer contracts. The process of securing applications involves various steps, such as threat modeling, security testing, and code review. This helps to identify and remediate vulnerabilities early in the development process, before they can be exploited by attackers. Regular security assessments can also help to identify any newly discovered vulnerabilities, and to ensure that the applications continue to meet the required security standards.